Traditional web scrapers rely on fixed selectors and predictable flows, working well in stable site environments but failing when websites update layouts, rebuild interfaces, or change the order of content loads. The Research and Markets reports show that the AI driven web scraping market will add USD 3.15 billion from 2024 to 2029. Analysts expect a compound annual growth rate of 39.4 percent over this period.
The web’s rapid evolution—through updates in layout, script-based content, and mixed formats—exposes these limitations.
AI fundamentally changes web scraping by treating pages as structured environments rather than just static HTML. AI development shapes how extraction engines learn structure, interpret context, and update logic. It interprets layouts, understands text, reads visuals, and navigates multi-step logic. Enterprises leverage these abilities for planning, pricing, forecasting, compliance, and reporting, turning public information into a continuous, instead of periodic, data source.
The growth of the AI-driven web scraping market is driven by expanding operational needs across sectors like retail, finance, logistics, insurance, AI development, and public-sector analytics. These industries rely on external signals as extensions of internal datasets. When website structures shift, older tools often fail, but AI maintains data continuity in changing environments.
This document describes the market outlook through 2030. It covers definitions, technology, adoption trends, security, regulations, competition, and long-term expectations. The analysis aims to offer non-technical leaders a strategic perspective.
“Architecture comes with compliance by design and full measurability. That stable base unlocks machine learning and process automation in real operations—logistics, healthcare, and beyond.”
— Eugene Yushenko, CEO
Definition and Market Scope
AI-powered web scraping uses systems equipped with machine learning, text analysis, visual interpretation, and language-based agents to collect structured web data.
These systems read changing interfaces, spot context, and follow exploration-like actions. AI-powered web scraping extends its reach through multi-modal methods described in Generative AI development, where models interpret mixed content and structural patterns.
They are used across product catalogs, regulatory documents, financial disclosures, news sites, technical content, and industry reports.
The category spans several capabilities:
Interpretation of dynamic structure
Models read layouts as evolving patterns, rather than fixed positions.
Understanding of text blocks and metadata
Systems extract fields, topics, and entities from varied content.
Recognition of images, diagrams, and charts
Visual layers convert graphics into structured values.
Navigation of multi-step processes
Agents complete forms, reach deeper pages, and follow branching paths.
AI trends in web scraping show an increased use of agent-like navigation, as described in AI chatbot development, where language models coordinate multi-step interactions with interfaces.
Automatic correction of common failures
AI detects broken flows and adjusts behavior to restore continuity.
Integration with business systems
Tools connect extracted data with pipelines, dashboards, and analytics environments.
Enterprises adopt these capabilities to maintain steady access to external signals. AI reduces maintenance effort in environments where websites load content via JavaScript or frequently change layout. It supports workloads that depend on uninterrupted collection.
Difference Between Traditional and AI-Powered Scraping
Traditional scrapers use fixed selectors and predefined rules. They work when pages remain unchanged. Even minor layout updates break their logic.
Maintenance requires manual updates, which increase operational costs.
AI-driven tools interpret meaning rather than position. They locate relevant elements by relationships, context, and structure. They follow instructions written in natural language and adapt when flows shift. They remain stable when developers redesign interfaces or restructure pages.
“My strategy is to translate complex business needs into a cloud-native infrastructure that holds when traffic spikes, APIs drift, or new LLM models evolve. I ensure technical certainty from day one.”
— Dmytro Naumenko, CTO
This shift influences enterprise planning. Static scrapers depend on stable environments. AI-driven tools support operations in environments that change daily. This difference defines the long-term direction of the market.
Key Components of AI-Driven Scraping Technologies
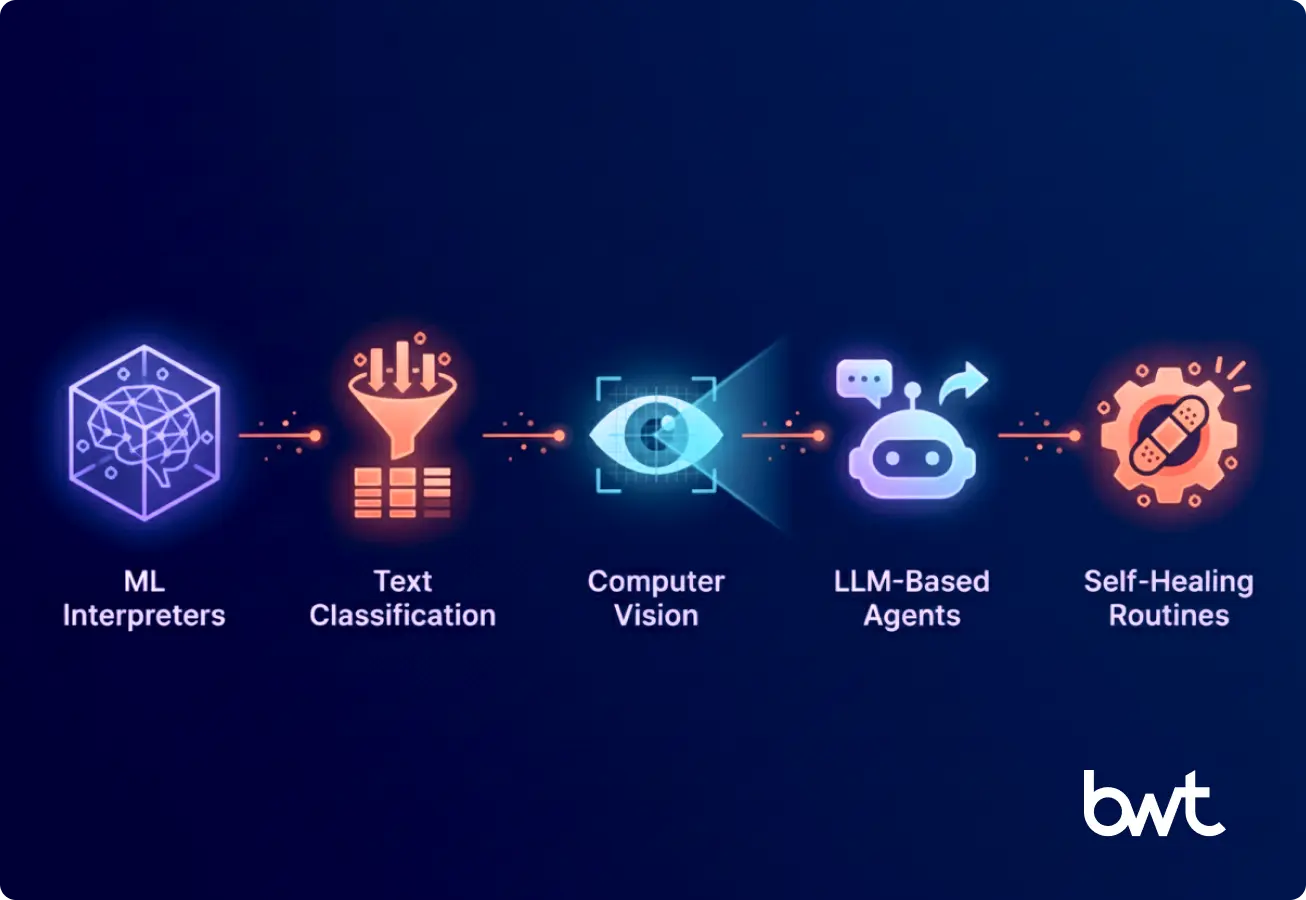
Resilient extraction depends on design. Models fail when the infrastructure does not account for variation, load, or interface change. GroupBWT builds systems that remain stable under pressure.
AI-driven extraction combines several layers. Each layer supports adaptability and reduces interruptions.
Machine Learning Interpreters
Models examine structure, detect patterns, and identify relationships among elements. They adapt when websites alter layout or move components. This reduces failures caused by small changes.
Text Classification
NLP models separate relevant content from surrounding noise. This capability aligns with methods presented in Natural Language Processing solutions, which strengthen AI-powered web scraping in text-heavy environments. They extract entities, terms, and metadata. They reduce volume and help teams focus on meaningful fields.
Computer Vision
Visual models read embedded text, icons, charts, and diagrams. They capture information placed inside images or graphical components. Many sites use visual elements for prices, attributes, or labels. AI vision ensures that this information stays accessible.
LLM-Based Agents
Agents follow language instructions and complete tasks across multi-step flows. They click elements, scroll pages, input values, and interact with menus. They behave flexibly and replace rigid scripts.
Self-Healing Routines
AI detects failures, identifies causes, and retries with revised actions. It restores activity without human intervention. Self-healing reduces downtime in large-scale environments that require continuous collection. These mechanisms follow principles outlined in AI for data scraping, which demonstrates how AI-powered scraping adapts to layout variation and execution drift.
Growth in AI driven scraping reflects a shift in which public data becomes part of the core decision-making layer in enterprise systems. When signals arrive on time, planning cycles speed up and decisions stay aligned with real conditions.
Architectural Discipline at GroupBWT
GroupBWT’s approach aligns with this view. Each engine incorporates interpreters, visual models, and autonomous agents. Self-healing logic detects broken flows, identifies causes, and restores activity. These layers reduce maintenance and protect continuity in environments that shift frequently. Alex reinforces this principle.
“Scraping systems do not fail because the code is weak. They fail because the design does not reflect how platforms behave. Our teams focus on systems that maintain activity through change and scale.”
— Alex Yudin, Head of Data Engineering
This architectural focus connects model capability with operational stability. It defines how GroupBWT implements AI-driven extraction in production environments.
Current Market Value: Enterprise Meaning
Retail tracks product movements and attribute changes. Finance follows disclosures and policy shifts. Logistics, manufacturing, and healthcare monitor sector updates. AI developers gather structured training input. These groups build pipelines that mix internal indicators with public signals. They treat external data as infrastructure, not as an occasional source. Such practices follow analytical frameworks for scraping in data science, which explain how AI-powered scraping supports modeling, trend detection, and forecasting.
This market growth shows that enterprises are moving toward stable extraction architectures. They aim to remove maintenance overload, control fragmentation, and support continuous ingestion. AI driven web scraping market data extraction meets these needs by interpreting structure, context, and behavior. It stays stable even as websites shift their layouts or load patterns. Teams gain predictable output and lower operational friction.
Steady double-digit growth through 2030 follows clear drivers:
- Web structure changes faster each year. AI updates its interpretation and keeps data flowing.
- Real-time signals shape daily pricing, planning, and compliance. Teams need current inputs.
- Manual maintenance adds cost. Static scripts break after layout changes. AI reduces this burden.
- Modern data platforms expect automated ingestion. AI extraction aligns with these workflows.
Market expansion signals a move toward pipelines built on agents rather than fixed selectors. AI extraction becomes a foundation for technical and operational teams that need continuity at scale.
Main Drivers of AI Web Scraping Adoption
AI reads structure, text, and visuals. It understands relationships between elements. It handles dynamic navigation and multi-step flows. These capabilities replace fragile instruction sets with adaptable reasoning. Enterprises gain stable pipelines that align with modern architectures.
Websites Update Constantly
Teams face frequent shifts in layout and loading behavior. AI models read patterns, understand relationships, and adapt. They protect continuity when platforms redesign their interfaces.
Public Signals Influence Enterprise Cycles
Planning, supply chain coordination, and compliance depend on accurate external information. AI-driven extraction provides the steady feed that internal models require.
Legacy Tools Break Under Pressure
Rule-based scripts fail when components move or the load order changes. Each failure triggers a delay. AI reduces interruptions through interpretation and recovery.
AI Protects Continuity
Models view a page as a dynamic structure. They track meaning, not fixed positions. This keeps output stable even during rapid UI evolution.
Enterprise Networks Grow More Complex
Teams operate across multi-cloud setups and distributed systems. AI agents coordinate extraction across environments and maintain activity during structural changes.
How Companies Move from Rules to Agents
Enterprises follow a three-step transition:
- Rules: Teams rely on selectors, XPaths, and predictable flows.
- ML-assisted interpretation: Models detect layout patterns and adjust logic when sites shift.
- Autonomous agents: Agents follow language instructions, explore flows, recover from failure, and coordinate extraction across systems.
This transition mirrors the broader shift in enterprise AI adoption. AI trends in web scraping include instruction-based agents described in how to use ChatGPT to fully automate web scraping, where systems recover from failures through adaptive reasoning. Extraction moves from manual repair toward autonomous, self-adjusting operation.
Key AI Technologies Transforming the Market

AI reshapes how organizations collect, process, and store web-based information.
Machine Learning for Dynamic DOM Understanding
Models view a page as a structure that evolves over time. They identify patterns and update their interpretation when changes appear.
NLP for Context and Content
NLP extracts fields, topics, and key terms. It helps teams analyze sentiment, follow competitor updates, and review regulatory changes.
Computer Vision for UI Interpretation
Vision models convert images and charts into structured values. They handle complex layouts that mix visuals with text.
LLM-Based Autonomous Agents
Agents follow instructions and complete flows through flexible logic. They reach deeper sections and adapt to new structures. These recovery patterns reflect logic described in LLM for web scraping, where models handle structural change through contextual interpretation.
Self-Healing Logic
Automation identifies broken paths, corrects actions, and preserves continuity. It reduces manual intervention and supports stable pipelines.
These technologies form the foundation of AI-driven extraction.
Core Use Cases of AI-Driven Web Scraping
AI-driven extraction supports many enterprise activities.
Market Intelligence and Competitor Monitoring
Teams follow catalog updates, pricing changes, and product launches. These signals guide planning and strategic decisions.
E-Commerce Pricing and Product Analytics
Retail units track stock levels, seasonal changes, and attribute updates. They adjust pricing strategies based on observed movement.
Financial Market Insights and Alternative Data
Investment teams gather disclosures, sector news, and public statements. These signals support risk review and market analysis.
Data for AI and Machine Learning
AI developers require large datasets: AI-driven extraction supplies text, images, and metadata for training and evaluation.
News, Sentiment, and Social Media Analysis
Analysts track conversation patterns, tone shifts, and emerging topics.
Compliance and Regulatory Intelligence
Legal teams monitor updates, notices, and policy changes across jurisdictions.
Use cases grow as organizations integrate external data into daily operations.
GroupBWT in Practice: How AI-Driven Extraction Works in Real Projects
AI-driven extraction gains value when models, agents, and infrastructure operate as one system. GroupBWT applies this approach across projects that require continuity, resilience, and full traceability. Our teams build extraction engines that interpret structure, manage variation, and maintain activity during rapid interface change.
E-Commerce Competitive Intelligence
A logistics client needed a stable feed of pricing and availability from hundreds of retail sites. Layouts changed weekly, and anti-bot controls varied. Rule-based scrapers failed often and required frequent updates.
GroupBWT built an AI-driven extraction system with interpreters, visual models, and autonomous agents. The system recognized page shifts, recovered broken flows, and updated logic without manual work. Maintenance effort decreased by eighty-five percent. The client aligned pricing with real market movement and shortened planning cycles.
Retail Product Analytics
A global retailer monitored attribute changes across diverse catalogs. Many sites mixed images, icons, and dynamic blocks. Traditional scrapers lost context when components moved.GroupBWT deployed a multi-modal pipeline that combined DOM analysis, NLP, and computer vision. Models extracted attributes from both text and embedded visuals. This design stabilized the output and increased field coverage across seasonal and regional variations.
Financial and Regulatory Intelligence
A fintech company tracked disclosures, regulatory updates, and public filings. Structures changed often, and noise from surrounding content created uncertainty. GroupBWT designed an extraction architecture with strict field controls, provenance logs, and sensitive-data filters. NLP models separated material sections from irrelevant text. The client gained reliable signals for risk review and compliance work.
AI Training Data for Model Development
AI teams required structured datasets for model training. Sources included product pages, technical documents, and mixed-format environments.
GroupBWT built a pipeline that combined language agents and pattern detectors. The system interpreted structure and extracted multi-level fields. Clean data supported model evaluation and reduced manual labeling.
These examples show how AI-driven extraction supports real operations. They demonstrate the impact of architecture that interprets structure, manages variation, and maintains continuity at scale.
Industry Breakdown: Who Uses AI Web Scraping
AI-powered extraction supports sectors that rely on current public information.
Retail and E-Commerce
Teams analyze product attributes, pricing, and seasonal patterns.
Finance and Fintech
Teams track risk indicators, compliance updates, and market shifts.
AI and ML Product Companies
Developers gather material to improve model accuracy and coverage.
Data Vendors and Aggregators
Vendors supply structured datasets to clients through internal pipelines.
Enterprise Analytics and BI
Analytics teams blend internal and external signals to support reporting.
Any function that depends on external information benefits from AI-driven extraction.
Sector-level adoption expands when organizations apply insights from the impact of AI chatbots in industries, which explains how conversational models support AI-powered web scraping in operational settings.
Market Challenges and Limitations
AI enhances capability but introduces new responsibilities. Teams evaluate these responsibilities using guidance outlined in web scraping challenges and their mitigation strategies.
Anti-Bot Systems and Dynamic Interfaces
Websites use behavioral detection and scripted loading. AI navigates these patterns through adaptive logic.
Noise and Inconsistency
Public data varies in quality. AI reduces noise but requires human review for critical tasks.
Scalability and Infrastructure Costs
Large-scale extraction demands compute resources, routing logic, and distributed processing. AI reduces maintenance but still depends on infrastructure.
Organizations balance capability with operational and compliance requirements. These requirements match the engineering expectations of web scraping, which outlines stable architectures for production-grade extraction workloads.
Security Pressure: The New Layer of Operational Risk

AI-driven systems introduce new behavior patterns that differ from conventional bots. They follow instructions, adapt to layout changes, and move through multi-step flows. These patterns change how platforms classify traffic, creating a need for transparent governance. They do not create problems by default. Proper configuration keeps activity predictable and aligned with enterprise standards.
AI-driven systems show several traits:
- Irregular schedules: Agents run based on instructions, not fixed time slots.
- Distributed origins: Traffic comes from varied regions and cloud networks.
- Language-guided navigation: Agents follow prompts that define exploration paths.
- Human-like interactions: They scroll and click through layered flows.
- Feedback-driven adaptation: They adjust actions when interfaces shift.
These traits increase load only when extraction lacks governance. A single instruction may trigger several internal steps, yet well-configured systems use rate limits, routing rules, and clear boundaries to control downstream activity. With these controls in place, AI-driven extraction remains stable and predictable.
Why This Matters
Enterprises need an extraction that supports clarity, control, and compliance.
- Network resources: Traffic stays within defined limits when rate rules guide activity.
- Cloud usage: Workflows remain efficient when orchestration policies manage execution.
- Backend stability: Controlled extraction protects user-facing systems.
- Monitoring: Clear agent signatures simplify security oversight.
- Governance: Boundaries separate automated flows from human traffic.
GroupBWT designs extraction architectures that apply these controls from the start. Rate limits, routing logic, and governance policies ensure that AI-driven systems operate safely and predictably inside enterprise environments.
Regulatory and Ethical Landscape
Regulation shapes practices around public data collection.
Privacy Rules
Teams manage sensitive fields carefully. They remove personal information and follow internal review protocols.
Fair Use
Public access does not guarantee broad usage rights. Jurisdictions interpret data reuse differently.
Responsible AI and Provenance
Organizations track sources, document accuracy, and maintain clear provenance. Transparency strengthens internal governance and external communication.
Industry Movement Toward Clarity
Vendors improve documentation. Enterprises expect transparent sourcing. This trend reduces compliance risk and supports trust among partners.
Future Outlook: Where the Market Heads by 2030
AI-powered extraction will become more deeply integrated into enterprise data systems. Several developments define the period through 2030.
AI Orchestration and Autonomous Agents
Multi-agent systems coordinate tasks, complete flows, and reduce oversight. They optimize extraction paths and distribute logic.
Integration with Data Engineering
Extraction connects directly to internal pipelines, feature stores, and reporting tools. This shortens the time of data collection and action.
Multi-Modal Extraction
Systems process text, images, and structure as unified inputs. This expands coverage across diverse environments.
Shift Toward AI-Only Extraction
Script-based tools remain for narrow tasks. AI-driven tools support broad workloads and changing interfaces.
Conclusion: Why AI-Driven Web Scraping Becomes a Core Strategy
AI-powered extraction supports continuity in rapidly changing environments. It reduces maintenance effort, improves stability, and aligns data collection with modern operational needs.
Enterprises follow strict limits on what can be collected, processed, and stored. Pages often contain fields that teams must avoid, such as emails, phone numbers, private identifiers, medical details, and any data that links a profile to a person.
GroupBWT manages this through allowed-source mapping, predefined field lists, automated PII removal, and provenance logs that track origin and transformations.
Best practices include sensitive-field filters, domain allowlists, traffic controls, and separated storage for regulated information. These measures keep extraction safe, auditable, and aligned with enterprise compliance. Leadership benchmark other capabilities using the criteria reviewed in the best companies for web data extraction, which compares providers across architecture, governance, and resilience.
AI-driven web scraping becomes a core enterprise capability because it supports continuous access to current external signals and helps organizations respond to changing conditions.
FAQ
-
Which industries gain the most substantial benefits from AI-driven web scraping?
Retail, finance, logistics, insurance, analytics, and AI development depend on timely external data. These teams monitor market movements, review pricing signals, and manage risk through structured outputs. Data vendors also rely on stable extraction to deliver consistent datasets to clients.
-
How accurate is AI-based extraction in real enterprise conditions?
Accuracy reflects model design, site layout, and consistency across source environments. Teams strengthen reliability through targeted sampling, clear labeling rules, and scheduled audits. This approach keeps outputs steady when interfaces evolve.
-
What steps help enterprises adopt AI-driven scraping securely and compliantly?
Teams identify permitted sources, set usage boundaries, and map sensitive fields. Security units apply rate limits, classify automated activity, and monitor access patterns. A pilot phase confirms stability before expanding extraction across departments.
-
How should executives evaluate and select AI web scraping vendors?
Leaders review extraction stability, governance features, and sourcing clarity. Vendors should provide transparent logs, consistent recovery paths, and documented integration methods to support quality, update cadence, and alignment with compliance, guiding the final choice.
-
Which ROI metrics help measure value from AI-driven extraction?
Teams monitor maintenance effort, error frequency, and time-to-insight. Executives evaluate how extraction shortens planning cycles and reduces operational delays. Stable activity also lowers support requirements.
-
How can organizations reduce operational, legal, and reputational risk?
Teams maintain source lists, apply rate controls, and document provenance. Compliance units review sensitive information, approve restricted fields, and maintain audit records. Security teams classify automated agents, isolate anomalies, and enforce traffic policies.
-
How does AI-driven extraction integrate with enterprise data pipelines?
Data moves through API layers, staging zones, and reporting environments. Pipelines ingest structured outputs and align them with analytics and forecasting tools. This process links collection, interpretation, and business decisions.