Retail leaders need clear and fresh product signals to guide pricing, supply, and assortment decisions. Public Aldi interfaces expose structured information that supports these workflows.
Many search queries refer to Aldi app scraping, yet the relevant data flows through web endpoints used by the website and the mobile interface.
This guide explains how to scrape Aldi data, interpret the results, and design a compliant pipeline to support stable analytics.
Strategic Context: How Aldi App Scraping Supports Retail Planning
Retail teams track prices, promotions, stock shifts, and assortment changes. Aldi scraping converts public product fields into structured signals that help leaders manage weekly retail rhythms. To fully capitalize on these trends, companies often implement dedicated retail data scraping pipelines that aggregate signals from multiple competitors.
Pricing Signals That Guide Margin and Market Response
Pricing moves quickly across Aldi regions. Teams collect public price data and study week-to-week differences. These patterns highlight margin exposure and pressure points in category corridors. This work strengthens decisions across planning cycles. For example, deploying a custom web scraping solution for tackling competition allows firms to flag undercutting strategies in real-time automatically.
Promotion Signals That Shape Category Dynamics
Weekly offers influence demand and basket structure. Aldi scraping captures promotion timing, discount depth, and visibility. Analysts forecast promotional lift and align marketing actions with observed shifts.
Assortment Signals That Reveal Category Intent
Aldi rotates seasonal goods and introduces limited-time items. Public fields display new entries, delisted SKUs, and assortment updates. These records help planners understand category intent and track assortment churn.
Stock Signals That Support Supply Coordination
Visible stock markers provide early demand cues. Repeated low-stock states signal pressure on specific SKUs or regions. Supply teams use these signals to coordinate replenishment decisions.
These four signal groups anchor the business case for Aldi app scraping and prepare teams for the compliance layer.
“Retail teams gain clarity only when fresh product data moves through predictable, governed pipelines. Without this discipline, even strong signals lose their value.”
— Alex Yudin, Data/Web Scraping Engineer at GroupBWT
Compliance Foundations Before Starting Aldi Application Scraping
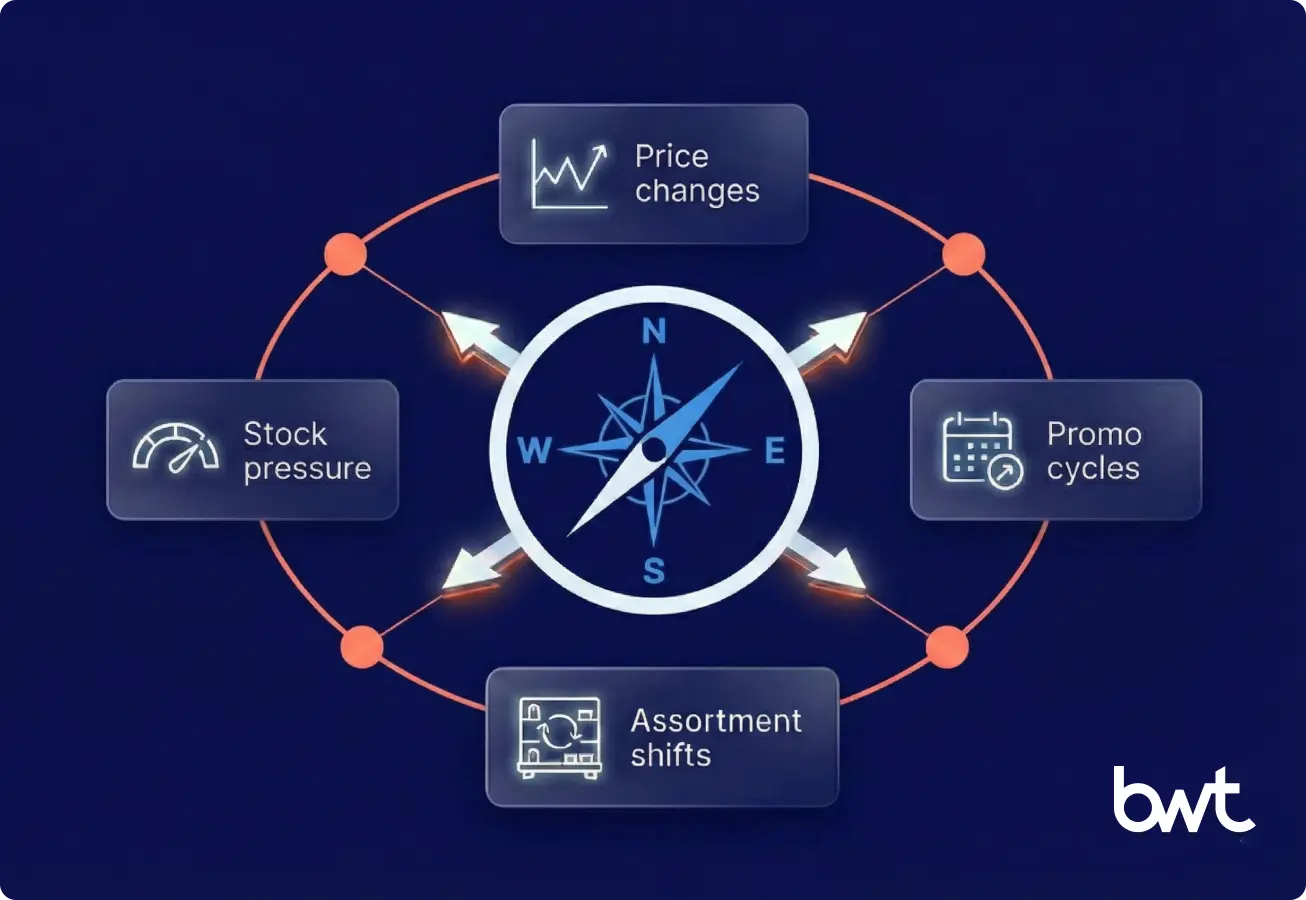
Compliance governs every extraction step. Leaders define boundaries that protect legal position, infrastructure stability, and internal governance rules. This framing ensures Aldi scraping operates as an analytical workflow, not a high-volume harvesting system.
Legal Review of Robots.txt and Contractual Boundaries
Teams read robots.txt to identify allowed paths. This step sets clear expectations for navigation, selectors, and request planning.
Operational Rules That Protect Infrastructure
Teams design low-frequency request patterns. They spread activity across longer intervals and limit concurrency. These steps reduce load and keep traffic safe for real users.
Intellectual Property and Data Usage Controls
Analysts extract factual fields only. They avoid storing images, extended creative descriptions, or protected brand material.
Governance Expectations Inside the Organization
Internal teams document purpose, allowed fields, and expected update cycles. They validate that requests align with approved policies and operate within permitted scope.
This compliance frame prepares the team to define the public fields available for analysis.
Public Aldi Fields: What Teams Can Safely Extract
Aldi regions consistently present factual elements on public pages. These fields provide the foundation for modeling the Aldi dataset for web scraping and downstream analysis.
Core Public Fields That Support Retail Analysis
Product titles, package sizes, standard prices, unit prices, promotion markers, stock indicators, nutrition tables, ingredient lists, and basic location metadata.
These factual elements support dashboards, forecasting, and category evaluations.
“Retail decisions move fast, so the data foundation must stay simple and stable. When product fields stay clean, every pricing, promotion, and assortment model becomes easier to trust and explain.”
— Olesia Holovko, CMO at GroupBWT
How to Scrape Aldi Supermarket Data Safely and Predictably
A straightforward workflow protects infrastructure while delivering reliable signals. The following sequence supports safe operations and stable results.
Scope Definition Before Traffic Moves
Teams define the narrowest viable target. They choose a region, a category, or a SKU list. This focus limits load and improves selector accuracy.
Safe Navigation Aligned with Allowed Paths
Teams follow robots.txt rules and restrict activity to approved areas. This step shapes URL patterns and navigation logic.
Low-Frequency Request Patterns for Stability
Teams run controlled intervals between requests. This keeps traffic predictable and reduces the number of rate-limit triggers.
Rendering Actions That Reveal Dynamic Public Fields
Aldi uses JavaScript to load prices, stock, and structured elements. A headless browser renders these elements and safely exposes their factual fields. While this guide focuses on web endpoints, engineers facing native mobile defenses should review specific protocols for mobile app data scraping.
Parsing Actions That Convert Pages into Records
Parsing actions convert each page into a clear record. Engineering teams read prices, units, sizes, titles, and stock cues. They use HTML parsing and structured metadata when the page exposes this information in a stable format.
Normalization Actions That Support Analytics
Normalization actions prepare the dataset for analysis. Engineers align units, timestamps, currencies, and weight values so each region shares the same structure.
Technical Architecture That Supports High-Quality Aldi Scraping
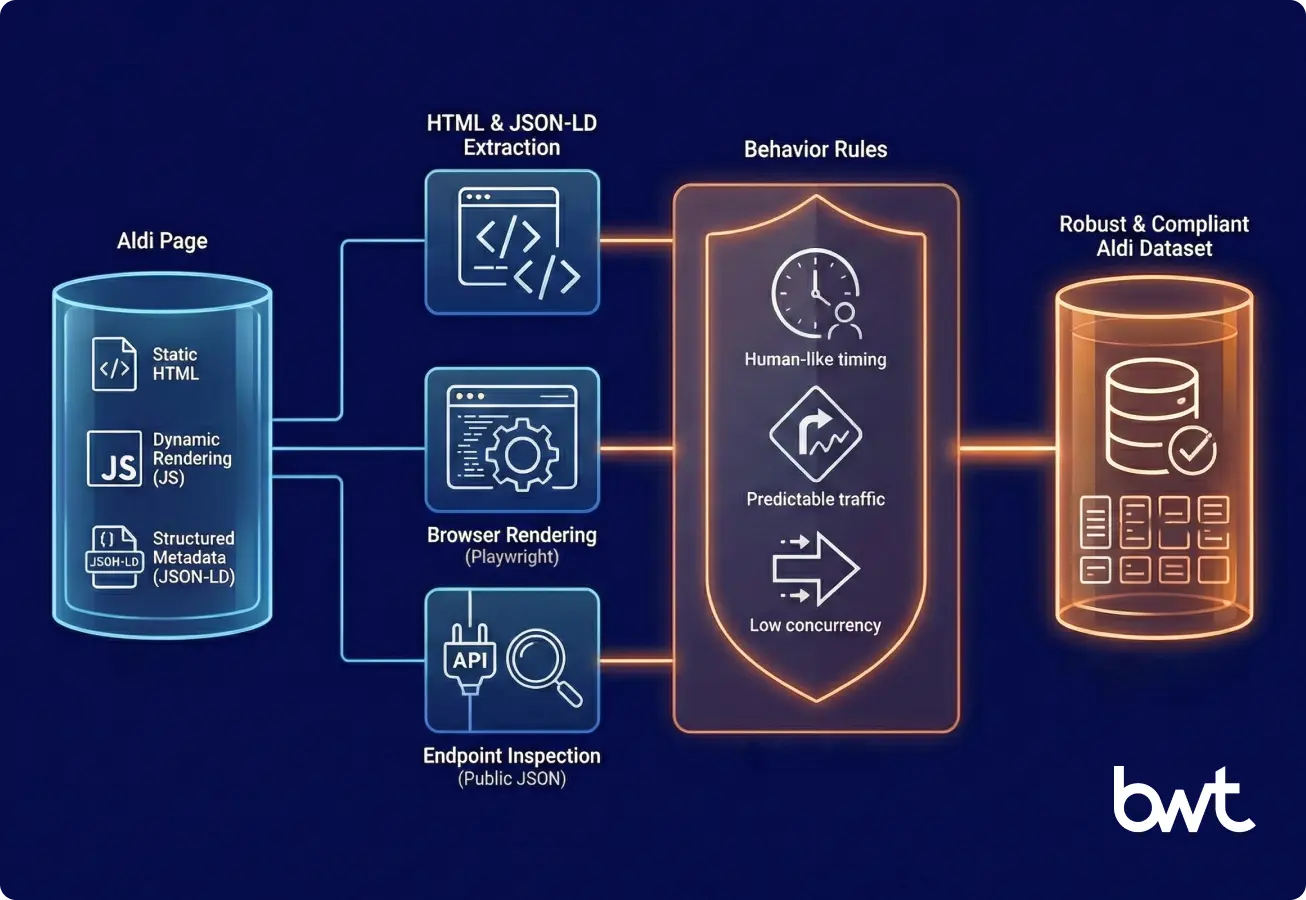
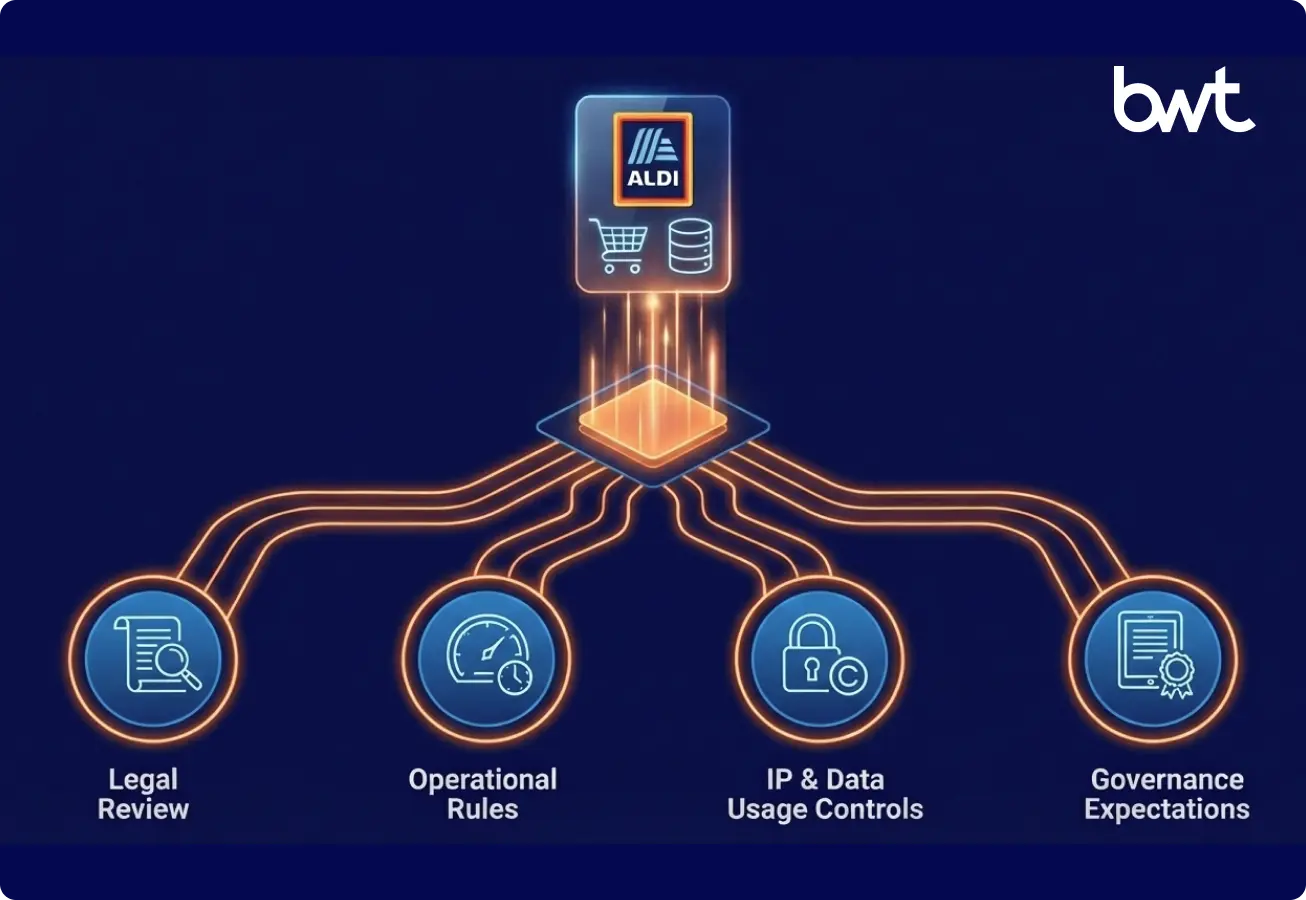
Engineering teams design the system that links compliance, extraction, and modeling. Aldi pages mix static HTML, dynamic rendering, and structured metadata. A resilient solution handles this variation and maintains strict controls.
HTML and JSON-LD Extraction for Structured Fields
HTML exposes titles, weights, and visible price elements. JSON-LD often shows brand, unit, and price values with strong accuracy. Engineers combine both sources to build complete records.
Endpoint Inspection for Allowed Public JSON
Some public pages load product JSON without any login. Engineers use this content only when it shows factual fields and follows the rules defined in the site’s access file.
Browser Rendering for Dynamic Values
Tools such as Playwright load dynamic price and stock elements. This guarantees completeness when Aldi updates its framework.
Comprehensive extraction strategies often require distinct approaches for different operating systems, such as specialized iOS app scraping techniques.
Similarly, accurate data collection from Google-based environments frequently necessitates dedicated Android app scraping configurations.
Behavior Rules That Reduce Anti-Bot Risk
Teams run human-like timing, predictable traffic, and low parallelism. These rules improve workflow stability.
This architectural stack supports robust Aldi app scraping while maintaining compliance boundaries.
Output Modeling: Structuring the Web Scraping Aldi Dataset
A clear model increases value for pricing, category, and supply teams. Clean field definitions show where each value comes from and help maintain compliance.
Schema That Captures Product, Region, and Time
Each dataset record includes product_id, timestamp, region_code, display_price, unit_price, inventory status, and metadata fields. This schema supports filtering, comparison, and long-term trend analysis.
Validation Rules That Maintain Data Integrity
Validation rules protect data quality. Engineers test price ranges, unit formats, timestamps, selector accuracy, and anomalies. These checks keep outputs reliable across regions.
Analytical Outputs Produced by Aldi Scraping
Once the dataset stabilizes, teams transform extracted fields into analytical signals.
Price, Promotion, Stock, and Assortment Outputs
Price movement timelines reveal trend direction. Promotion calendars show the timing and depth of discounts. Stock signals highlight regional demand surges. Assortment snapshots track new and removed SKUs.
Integrating these vast datasets is a core component of modern big data analytics in retail industry workflows. These outputs support weekly planning, forecasting, and operational alignment.
Safer Alternatives Before Adopting Aldi Application Scraping
Leaders often explore alternatives before building a technical workflow. Some needs are met through lower-risk sources.
Alternative Paths for Retail Product Signals
Retail teams compare public datasets, partner feeds, research reports, monitoring tools, and periodic manual checks. Each option provides signals without heavy traffic and may address broader planning needs. When internal resources are limited, partnering with professional mobile application scraping services ensures high uptime and legal compliance without the maintenance burden.
How to Scrape Aldi Data: Minimal and Compliant Example
The example below illustrates scraping Aldi data with a low-frequency browser request and simple parsing logic. It renders one page, extracts factual fields, and respects safe boundaries.
| from playwright.sync_api import sync_playwright
from selectolax.parser import HTMLParser import json def extract_jsonld(tree): script = tree.css_first(‘script[type=”application/ld+json”]’) if script: try: return json.loads(script.text(strip=True)) except Exception: return {} return {} def read_public_product(url): with sync_playwright() as p: browser = p.chromium.launch(headless=True) context = browser.new_context() page = context.new_page() page.goto(url, timeout=60000) html = page.content() tree = HTMLParser(html) data = extract_jsonld(tree) price = None if “offers” in data: price = data[“offers”].get(“price”) if not price: price_el = tree.css_first(‘[class*=”Price”], [class*=”price”], [data-test*=”price”]’) price = price_el.text(strip=True) if price_el else None title_el = tree.css_first(“h1”) title = title_el.text(strip=True) if title_el else None return {“title”: title, “price”: price} |
This example demonstrates a transparent, low-impact extraction aligned with governance rules.
Closing Perspective for Retail and Data Leaders
Retail teams depend on consistent signals for pricing, promotion, stock, and assortment planning.
Aldi app scraping supports these decisions when teams manage scope, request frequency, and compliance boundaries.
Engineers combine HTML parsing, JSON-LD extraction, controlled browser rendering, and allowed endpoint inspection.
Analysts model the output through clean schemas that maintain integrity across regions.
Leaders gain a predictable source of structured information to support better decisions and reduce uncertainty in dynamic retail environments.
“Structured data unlocks confidence. When teams see the same truth at the same moment, strategy accelerates, waste drops, and leaders act with clarity instead of guesswork.”
— Eugene Yushenko, CEO of GroupBWT
FAQ
-
How can teams integrate Aldi data into analytics pipelines or BI tools?
Engineering teams route validated records into a central warehouse layer. They publish structured product tables through focused data marts. BI platforms read these metrics to build dashboards. Pipelines add internal metrics, region attributes, and competitor benchmarks. This structure consistently reports and reduces maintenance across categories.
-
What practices help teams handle failed requests, markup shifts, or incomplete fields?
Engineers monitor extraction logs and isolate irregular records. They record snapshots of changed markup for fast debugging. Validation rules flag missing values and highlight selector drift. Lightweight monitors track structural shifts and alert teams before gaps spread across datasets.
-
How should teams choose between Aldi scraping and alternative data sources?
Leaders review business goals, update cycles, and operational load. Aldi data scraping supports localized insight and fresh signals. External datasets support a broader scope, fixed delivery rules, and predictable licensing. Teams choose the source that aligns with their planning horizon.
-
What technical or compliance risks appear when teams expand Aldi data extraction across regions?
Each region introduces unique URL patterns, timing rules, and rate expectations. Teams build region-specific queues, selector sets, and request schedules. Compliance reviews confirm that each region meets its own access requirements before traffic grows. This structure controls risk and maintains stable extraction.
-
How often should teams refresh Aldi data to balance insight quality and compliance?
Teams set renewal windows based on signal value. Pricing and promotions follow fixed weekly rhythms. Stock indicators change faster and require shorter cycles. Engineers design refresh plans that deliver timely signals without stressing target servers.
-
How to scrape Aldi supermarket data?
Teams scrape Aldi supermarket data by defining a narrow scope, following robots.txt, and using a headless browser to reveal dynamic public fields. They capture rendered pages, read HTML and JSON-LD for factual values, and convert each page into a structured record with strict validation. They normalize units, currencies, and regions so analysts can compare outputs across markets. This workflow keeps traffic controlled, maintains compliance, and produces a stable Aldi dataset.