Web scraping food-delivery data converts raw platform signals into structured, timely intelligence that guides pricing, streamlines operations, and directs expansion.
Understanding Web Scraping Food Delivery Data Requirements
Delivery platforms generate multiple streams of big data that reveal customer behavior, operational performance, and market coverage. Executives need to see how these streams fit together: customer sentiment shows loyalty risk, data points highlight market gaps, and platform-specific structures define the limits of comparability. When framed as a system, these elements move from technical detail to board-level signals about margin, speed, and competitive resilience.
Customer Sentiment as a Signal
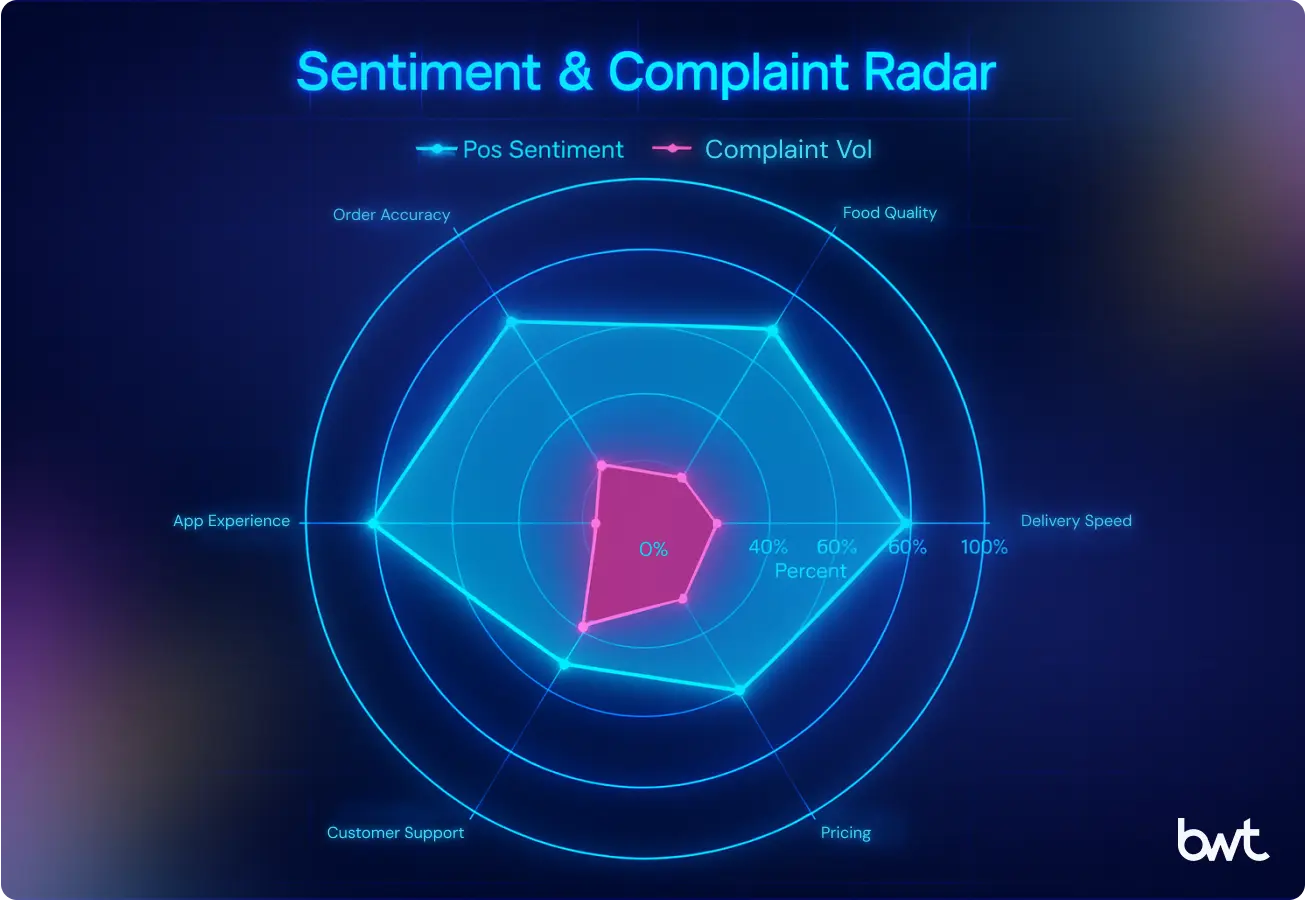
Customer sentiment drives competitive performance in food delivery. Positive reviews flag strengths in delivery speed and food quality, while complaints highlight pricing pressure and weak customer support. When scraped and analyzed, these signals warn executives where churn risk builds before revenue loss accelerates.
The Sentiment and Complaint Radar compares positive feedback with complaint volume across service factors: delivery speed, food quality, order accuracy, pricing, customer support, and app experience. This early warning system enables executives to correct operational issues quickly, preserving retention and revenue stability.
- The blue area represents positive customer sentiment.
- The red area represents the relative volume of complaints.
- A larger gap between blue and red shows stronger performance, while overlaps highlight friction points that require immediate attention.
This visualization makes it clear which service areas drive satisfaction and which ones are risk zones for customer churn. It demonstrates how structured sentiment analysis can be turned into actionable intelligence for improving operations, brand reputation, and customer experience.
Essential Data Points for Market Intelligence
Food delivery datasets include restaurant listings, menus, prices, delivery times, reviews, and geographic coverage. PwC’s Voice of the Consumer shows personalization built on multi-dimensional data can lift retention by 40%. For executives, that means fewer lost customers, lower acquisition spend, and stronger lifetime value.
Food Delivery Data Types and Strategic Value
| Data Type | Strategic Use | Executive Outcome |
| Restaurant Listings | Benchmark competitor coverage | Identify underserved zones |
| Menu Content | Track product cycles, sustainability claims | Shape R&D and marketing |
| Pricing & Fees | Monitor promotions and surcharges | Optimize dynamic pricing |
| Delivery Times | Measure operational reliability | Reduce churn risk |
| Reviews & Ratings | Capture customer sentiment | Strengthen brand loyalty |
| Geographic Coverage | Map market reach | Plan expansion investment |
Food delivery companies, like Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub, Deliveroo, etc., depend on distinct data formats and APIs. For instance, DoorDash alone controls 67% of the U.S. market, making standardization essential for valid cross-market comparisons. This standardization is efficiently managed through a custom-designed data aggregation framework that handles heterogeneous data sources.
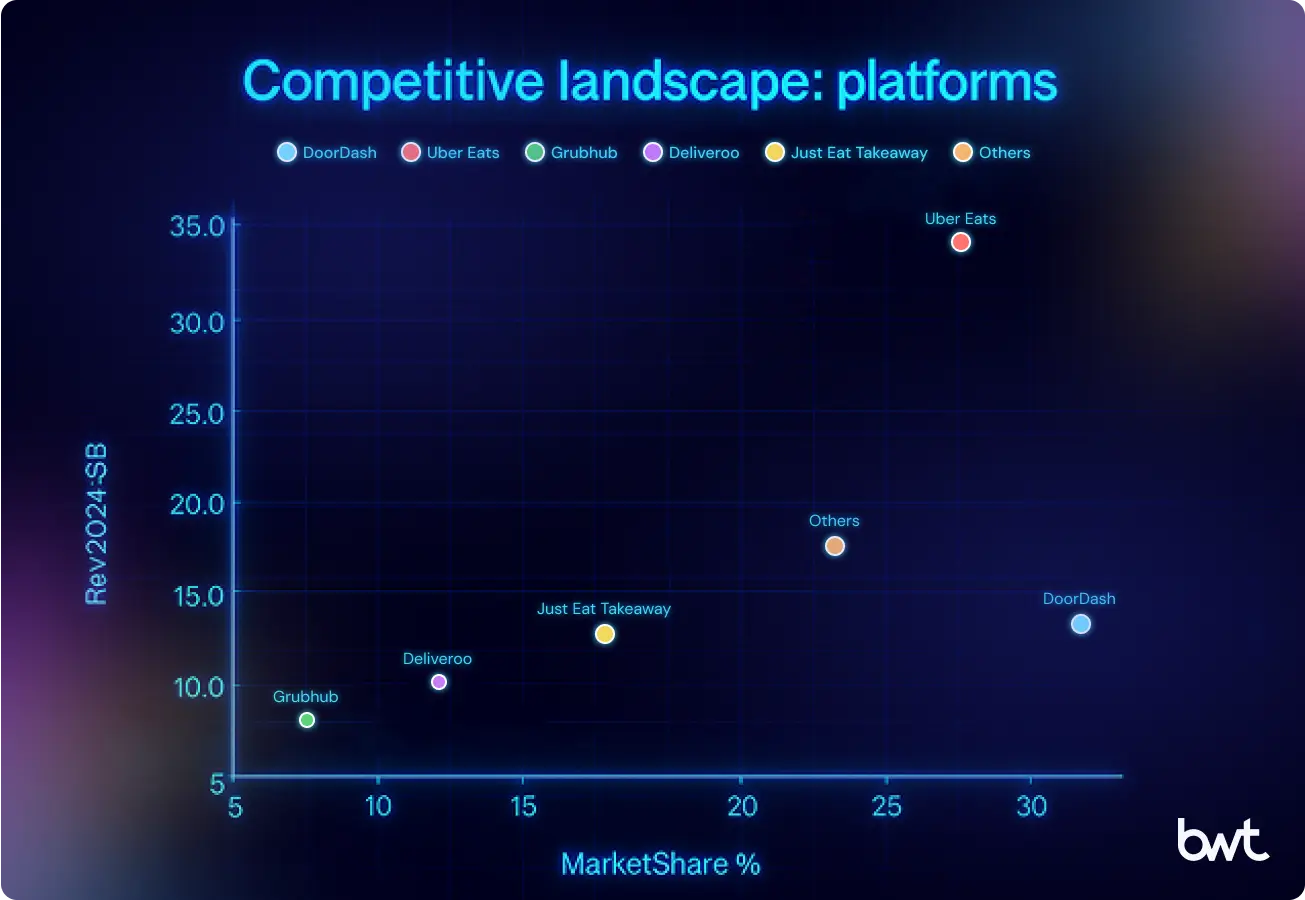
Parsing and standardizing their heterogeneous structures enables valid cross-market comparisons, which the OECD-FAO Outlook highlights as a growing barrier to global players.
Real-Time vs. Historical Data Collection
Historical datasets explain long-term consumption cycles. Real-time signals expose immediate demand shifts such as promotions, surges, or local shortages. According to the World Bank Digital Agriculture Playbook, integrating both live and historical data streams significantly improves forecasting accuracy and resilience.
Advanced Food Delivery App Data Scraping Techniques
Food delivery platforms now require advanced mobile app scraping services to capture dynamic menus, API-fed content, and geo-location signals. Resilient methods protect pipelines against API shifts and frequent JavaScript updates, ensuring continuous intelligence flow.
Scraping Challenges and Technical Solutions
| Challenge | Required Technique | Business Impact |
| Dynamic menus rendered via JavaScript | Headless browsers (e.g., Puppeteer) | Ensures complete menu capture |
| Mobile-first APIs | API orchestration layers | Standardizes data flow |
| Geo-locked content | Proxy rotation with geo-targeting | Enables cross-market visibility |
| Frequent platform updates | Modular crawler architecture | Reduces downtime, improves resilience |
| Rate limiting | Adaptive throttling | Preserves compliance and prevents bans |
Modern API Integration and Dynamic Content Handling
Traditional scraping methods—basic HTML parsing—no longer work effectively. Food delivery apps often render menus dynamically through JavaScript and mobile-first APIs. For these dynamic, often mobile-first sources, a key technical skill involves learning how to scrape data from mobile app interfaces and APIs directly.
Geo-Location and Multi-Market Data Collection
Cross-regional scraping is essential for benchmarking and global expansion. The World Bank Food Security Update shows that geographic segmentation of food systems directly affects competitiveness and supply resilience. Platforms in Asia-Pacific, which already capture 33% of the global market, highlight why cross-location scraping is a must for decision-makers. This collection frequently involves granular geo-data, making proficient data scraping from Google Maps a valuable skill set for market analysis.
Rate Limiting and Ethical Scraping Practices
Unregulated scraping risks IP bans and regulatory penalties. The European Commission Digital Markets Act Brief emphasizes the need for compliance with terms of service, GDPR, and local laws. Delivery platforms fined €329 million for anti-competitive practices show the financial stakes of neglecting compliance. Ethical methods—proxy rotation, rate limiting, and API-based integrations—ensure resilient and compliant operations.
Food-Delivery Data Scraping for Competitive Intelligence
Executives rely on web scraping food delivery data to anticipate pricing shifts and competitive launches.
Intelligence Streams and Strategic Applications
| Intelligence Type | Insight Provided | Executive Action |
| Price Monitoring | Competitor discount cycles | Adjust pricing dynamically |
| Menu Evolution | Seasonal or regional product shifts | Guide product launches |
| Delivery Zone Mapping | Gaps in competitor coverage | Target new market entries |
| Sentiment Analysis | Customer pain points | Prioritize service improvements |
| Inventory Signals | Demand volatility | Align procurement and staffing |
Price Monitoring and Dynamic Pricing Analysis
Food delivery operates in a high-frequency pricing environment. Scraped datasets enable tracking of competitor discounts, promotional cycles, and surge pricing. AI-driven dynamic pricing can lift upsell success rates by 28%. For executives, this translates into fewer missed revenue opportunities and stronger margin control.
Menu Trend Analysis and Product Innovation Tracking
Scraping menus over time reveals seasonal innovations, regional adaptations, and sustainability positioning. 92% of Gen Z rank sustainability as a top criterion in food choices. Capturing menu evolution enables teams to track competitors’ product innovation cycles and test market entry strategies with data-driven evidence.
Delivery Zone and Service Area Mapping
Coverage data shows which neighborhoods or cities are prioritized by competitors. Autonomous aerial deliveries are projected to handle 8% of orders by late 2025. Mapping service areas highlights where expansion can succeed or where competitor overextension creates gaps.
Implementing Food Delivery Data Scraping Infrastructure
Enterprises planning food delivery data scraping must design systems as core infrastructure. Often, the most efficient approach is data mining outsourcing to a specialized vendor who manages the entire infrastructure and maintenance lifecycle.
Scalable Architecture and Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-first food delivery data scraping supports elasticity and lower cost-per-record. Large-scale data pipelines need a cloud-first design. Lessons from cloud kitchens, which lower operating costs by up to 50%, inform how to design cost-efficient scraping systems. Executives who deploy custom web scraping solutions avoid brittle one-size-fits-all systems. These pipelines are optimized through data extraction services that focus purely on velocity and fidelity. When designing for large-scale mobile collection, engineering teams must consider an optimized Android data scraping service that bypasses platform restrictions.
Data Quality Assurance and Validation Frameworks
Scraped data often arrives incomplete or inconsistent. Validation across multiple sources prevents decision errors. With 95% of restaurants adopting AI-assisted operations in 2025, the need for clean, trustworthy input data grows urgent. Achieving superior output quality often relies on realizing the benefits of custom data aggregation tailored specifically to unique business logic.
The World Bank Food Systems Transformation Report frames quality assurance as a prerequisite for digital agriculture, equally valid for food delivery ecosystems. High-quality food delivery data scraping prevents schema drift and input corruption.
Integration with Analytics and Business Intelligence Platforms
Scraped data has limited value until it flows into analytics systems. Enterprises that connect scraping to business intelligence platforms report a 36% year-on-year lift in average order value through data-driven pricing and service insights. This data integration transforms raw feeds into actionable insights, a core function of sophisticated big data analytics in retail sector operations.
Infrastructure must support seamless ingestion into warehouses, dashboards, and forecasting engines to convert raw inputs into decisions that protect margin and accelerate speed of execution.
Data Governance and Future-Proofing Food Delivery Scraping Pipelines
Enterprises maintain scraping pipelines as part of permanent data infrastructure, audited and funded on the same cycle as warehouses and BI systems. Poor governance triggers cascading failures: data loses accuracy, systems degrade, and compliance exposure climbs. Executives need a governance framework that enforces resilience, adapts to platform change, and integrates with AI ecosystems.
| Dimension | Why It Matters | Outcome |
| Standardization | Normalizes mixed formats into BI/ML-ready inputs | Faster, cleaner insights |
| Schema Evolution | Handles frequent platform field changes | Lower maintenance cost |
| Security & Access | Controls sensitive reviews and geo-data | Compliance and risk control |
| Auditability | Tracks data lineage and source | Regulatory trust |
| AI Readiness | Prepares for integration with adaptive models | Future-proof pipelines |
This addition extends the article with a forward-looking lens that boards expect. It links scraping not only to current ROI but to long-term resilience, compliance, and AI adoption, which fits perfectly between infrastructure design and ROI discussion. The next evolution involves applying generative models, emphasizing the growing importance of AI data scraping to structure unstructured review content at scale.
Web Scraping Food Delivery Data Applications and ROI
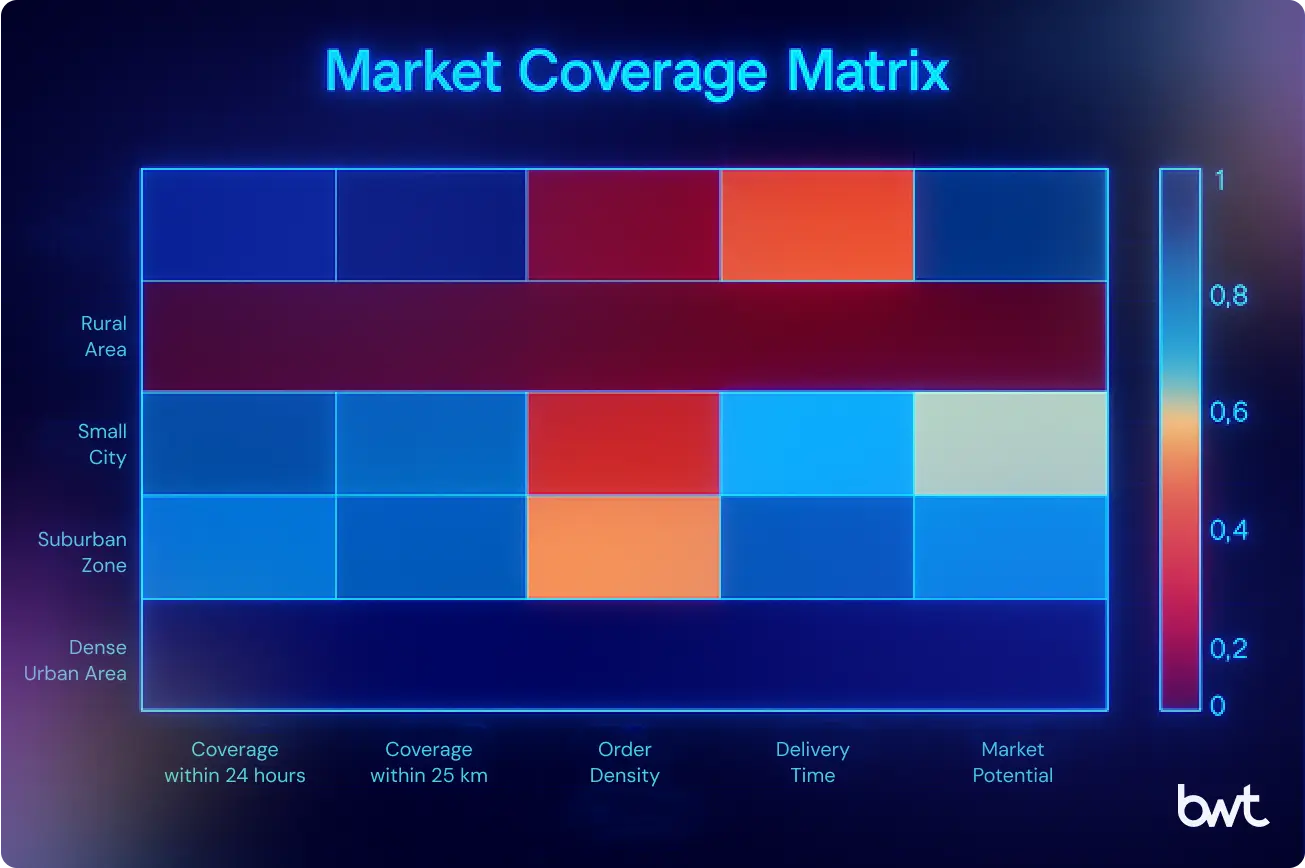
Food delivery platforms compete in fragmented markets where expansion choices shape margin and risk. Market coverage dictates how effectively platforms allocate riders, balance supply, and capture high-value customer segments. Executives treat this as an investment lens: gaps signal churn risk, while saturated zones compress margin through higher competition. Given the competitive pressure, leveraging specialized services like iOS scraping services ensures access to a full cross-section of consumer demand data.
The Market Coverage Matrix visualizes platform performance across five market types: food deserts, rural areas, small cities, suburbs, and dense urban centers. The horizontal axis shows operational metrics—coverage, order density, delivery time, and market potential. The vertical axis ranks market types. Color intensity marks performance: darker tones reflect stronger coverage or untapped potential, lighter or redder shades expose operational weakness or expansion risk.
Dense urban zones dominate most dimensions. Order density accelerates fleet utilization, and higher delivery frequency stabilizes unit economics. Suburbs and small cities perform moderately: coverage exists, but order concentration lags, creating margin pressure if logistics remain under-optimized. Rural and food desert areas remain underserved, where sparse demand inflates delivery costs and depresses ROI.
Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
Scraped order flows and pricing data enable AI-driven demand forecasting. Studies confirm that predictive models cut forecast errors by 20–50%. For food delivery, this means reducing overstock, aligning workforce allocation, and synchronizing with supplier chains.
Customer Sentiment Analysis and Brand Monitoring
Reviews and ratings provide high-frequency customer sentiment signals. 73% of consumers cite customer experience as a key buying factor. Scraping these signals at scale supports real-time service corrections and protects brand equity.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in Food Delivery App Data Scraping
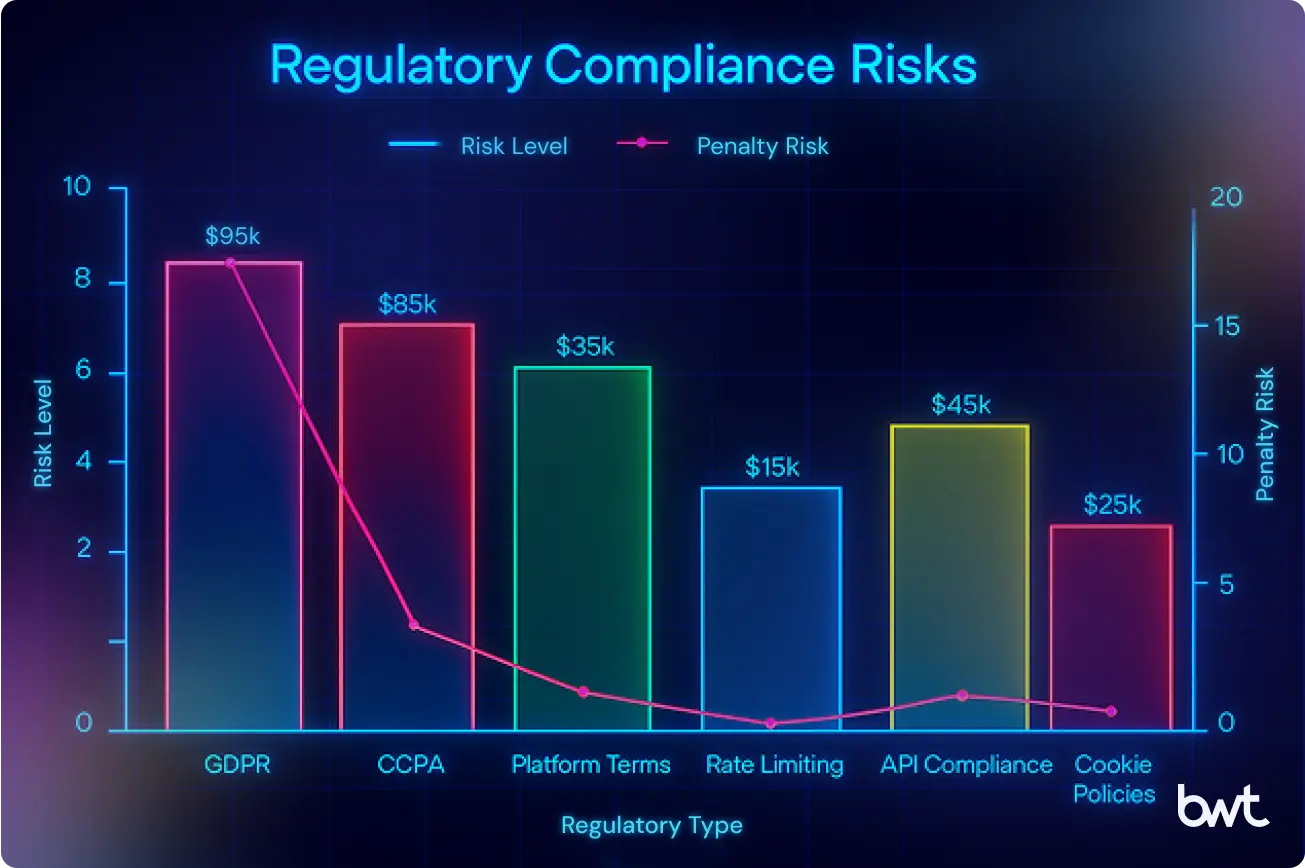
Food delivery app data scraping requires strict compliance with platform ToS and privacy law. Regulatory breaches carry direct financial penalties and operational risks. This chart highlights the most critical exposure areas, from GDPR and CCPA to API compliance and platform terms.
Platform Terms of Service and API Compliance
Each platform enforces restrictions on scraping. Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub define acceptable API calls and limit automated collection. The European Commission’s €329 million fine against Delivery Hero and Glovo shows how compliance lapses carry heavy financial consequences.
Data Protection and Privacy Regulations
Scraped data often contains personal identifiers like customer reviews linked to profiles. Regulations such as GDPR and CCPA demand strict safeguards. The European Commission’s Food Safety and Digital Standards outline compliance principles for handling sensitive food-related data. This framework can guide governance models for the delivery of data pipelines. The capability to scrape data from mobile app sources is crucial for obtaining the full legal picture of how data is presented to consumers.
Industry Best Practices and Ethical Guidelines
Leaders who anchor strategy in European Commission rules and OECD ethics frameworks convert compliance into a defensive moat. What others see as cost functions as insurance against disruption, fines, and reputational erosion.
Data collection moved into core capability status as firms tied it to compliance, forecasting, and automation. In markets defined by AI-driven personalization, automated delivery, and consolidation of global players, the firms that treat data pipelines as company-wide assets outperform those that treat them as side projects. Strong architectures combine adaptability with ethical safeguards and foresight.
Executives classify scraping pipelines as core infrastructure. When food-delivery data enters the asset register, it receives the same protection and planning as supply chains or payment rails. This shift secures three outcomes: continuous operations despite platform change, lower compliance exposure through controlled access, and faster adaptation to demand signals. The business gain comes from stable, uninterrupted scraping operations that maintain compliance and reduce downtime costs.
Wine Review Scraping for an Investment Platform: GroupBWT Case Study
A leading global wine investment firm required continuous monitoring of critic reviews to support portfolio decisions. Reviews published across diverse platforms shaped investor sentiment and directly influenced wine valuation. Manual tracking proved unsustainable as volumes scaled.
Solution
The engineering team built a scraping system capable of capturing, parsing, and normalizing reviews from multiple critic websites. The system is integrated:
- Python / Scrapy for scalable crawlers, optimized for structured review data.
- Node.js + TypeScript for orchestration and API endpoints.
- Puppeteer to render JavaScript-heavy review portals.
- MySQL is the central repository, ensuring queryable, reliable storage.
- Docker containers for deployment and environment consistency.
Outcome
The platform gained near real-time visibility into critical sentiment. Investment managers could benchmark wines, track changing evaluations, and align buying recommendations with current market views.
Similar GroupBWT case studies highlight how structured scraping pipelines deliver quantifiable outcomes across retail, manufacturing, and foodtech sectors. This success underscores the value of structured solutions, such as those provided by the data pipelines for food delivery company case study.
Boards treating web scraping food delivery data as infrastructure secure visibility into markets. Enterprises treating food delivery intelligence as a core capability should invest in enterprise-grade web scraping services to achieve resilience, compliance, and ROI. Investment in custom food delivery data scraping solutions enables predictive insights and resilience.
FAQ
-
How does food delivery data scraping improve decision-making?
Executives gain a live view of menus, pricing, reviews, and delivery zones. Teams operate on current signals instead of static reports. This shortens the decision loop and reduces lag between customer demand and organizational response. Faster adaptation improves pricing precision, delivery coverage, and customer retention.
-
What legal considerations should executives keep in mind?
Legal teams enforce platform terms and data protection laws. Scraping programs must align with governance frameworks to ensure compliance. Missteps risk fines, reputational loss, and platform restrictions. Proper design protects continuity: compliant systems build credibility with regulators, partners, and customers.
-
Which business areas gain the most value from web scraping food delivery data?
Pricing, service coverage, and customer experience capture the most measurable value. Pricing teams recalibrate strategies in near real time. Operations track delivery zone gaps and improve logistics efficiency. Marketing evaluates sentiment at the level of delivery speed, food quality, and app usability. Shared data streams prevent silos and create cross-functional alignment.
-
What makes food delivery app data scraping technically complex?
Engineering teams face shifting layouts, unstable data structures, and regional platform differences. Reviews, menus, and location data arrive in formats that change without notice. Systems require flexible architectures that normalize data and maintain consistency across geographies. Without adaptability, executives risk incomplete intelligence and distorted benchmarks.
-
How does food delivery scraping connect with strategic planning?
Scraping reveals competitor expansion patterns, product performance, and shifts in customer response. Strategy teams embed these signals into market entry, investment planning, and product development. Continuous pipelines move insights from raw platform activity into boardroom planning cycles. Strong architectures transform data collection from a tactical project into a core strategic capability.