Don’t just scrape tenders—structure them. We build custom systems that turn fragmented procurement big data into a unified, compliant, and searchable asset aligned with your jurisdiction and oversight needs.
Why Tender Data Aggregation Matters
Procurement systems rarely speak the same language. Disparate formats, portals, and procedures make it nearly impossible to gain a unified view of supplier behavior or contract patterns. Tender aggregation solves this by creating a single logic layer across procurement sources—local, national, and cross-border.
Procurement Still Lacks a Unified View
Most public procurement teams work with fragmented data. Notices, amendments, and award results are often published on separate portals, in different formats, and with inconsistent fields. Even basic indicators like CPV codes or contract values can be missing or delayed.
Some agencies still use PDFs or scanned documents, making the data nearly unusable for structured analysis.
Amendments are frequently detached from their original notices, breaking the logic chain between contract versions. Without structured data aggregation, it’s impossible to reconstruct contract histories, detect pricing anomalies, or audit award decisions at scale.
“We couldn’t even track whether the supplier had been selected before for similar work — the data was incomplete or scattered.”
— Procurement Data Analyst, Local Government
Aggregation Fixes Hidden Gaps in Oversight
A well-structured tender aggregation system links every contract element across jurisdictions, from first notice to final payment milestone. Once ingested and validated:
- Supplier profiles can be matched across regions and agencies
- Repeat issues (e.g., single-bid awards or mid-contract amendments) can be flagged
- Spend data becomes time-aligned, category-tagged, and audit-ready
This makes it possible to benchmark contractor performance, assess legal compliance, and detect emerging procurement risks. Effective oversight requires specialized solutions that leverage massive datasets, highlighting the evolving importance of big data in the legal industry for regulatory compliance.
Even the most advanced analytics platforms misfire if fed with partial or siloed data. Aggregation is not optional — it’s foundational.
Aggregated Tender Data Enables Action
When data is normalized and deduplicated across sources, procurement teams can:
- Build dashboards that reflect actual supplier behavior
- Monitor budget utilization across departments
- Track procurement process delays and legal blockages
Instead of reacting to fragmented insights, public sector teams gain a system-level view of procurement health, helping them prioritize reviews, flag inconsistencies, and justify decisions. The output of this structure is critical for advanced tools used in big data analytics for BI platforms.
If this sounds familiar, you’re not alone.
Many teams rely on tools that visualize broken data, not fix it.
Get Jurisdiction-Ready Procurement Intelligence
GroupBWT builds structured aggregation flows for national and cross-border procurement.
Systems are tailored to each country’s legal context, portal logic, and file structure.
Challenges in the Aggregation of Tender Data
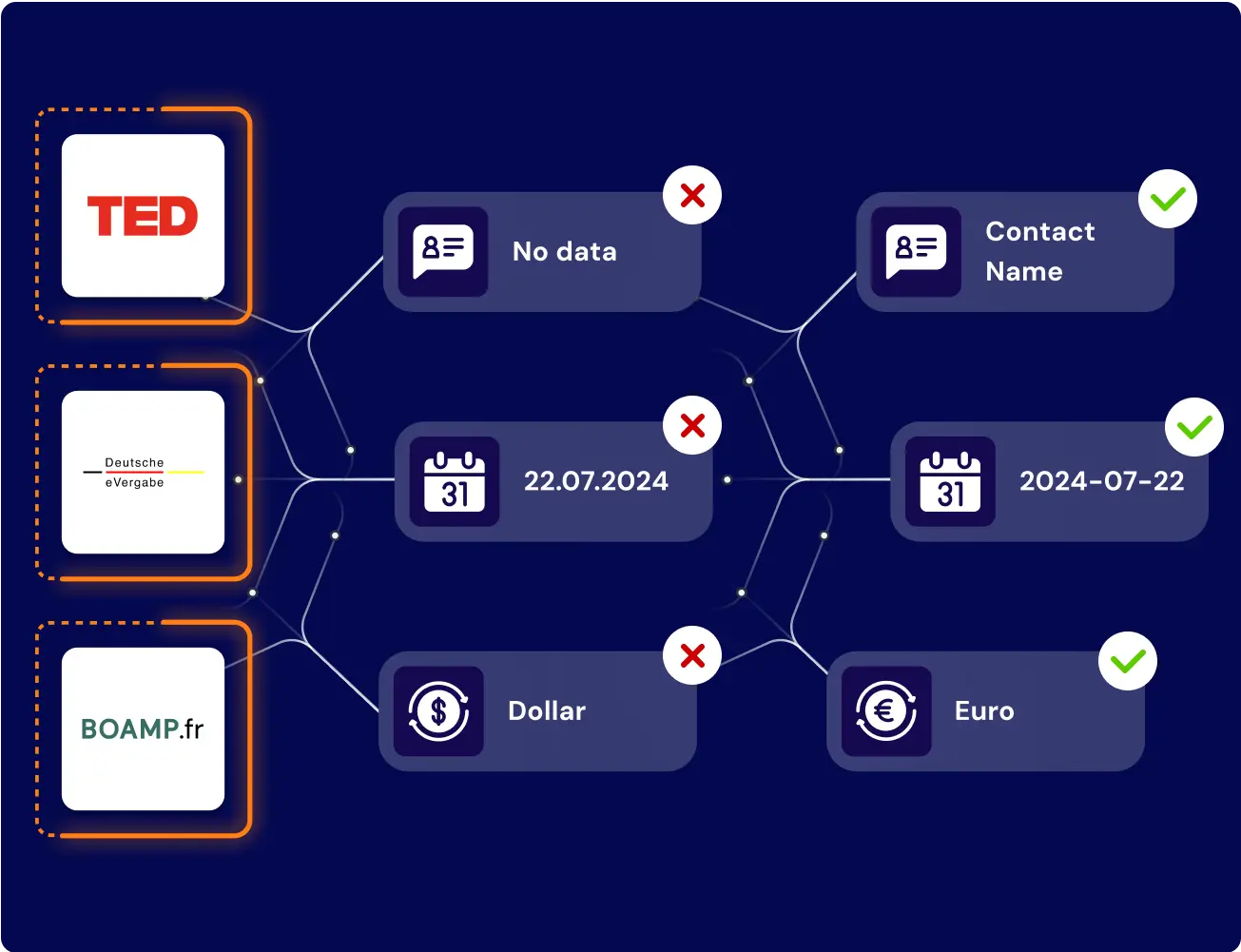
Aggregating tender data isn’t just about pulling files from different portals. It’s about aligning data with procurement rules, thresholds, and compliance standards that differ across jurisdictions. Even when notices are technically available, the structure behind them is often fragmented or incompatible.
What looks like a simple CSV export usually hides dozens of schema mismatches, missing fields, and legal constraints.
Aggregating across fragmented portals is the core challenge in public procurement data aggregation, especially when each source applies different structural and legal rules.
No Single Procurement Standard Exists
Despite EU-level directives and eForms initiatives, local authorities often publish tenders in formats that reflect legacy systems or internal logic.
- Some publish in PDFs or scanned documents, others in XML or JSON with custom schemas.
- CPV codes are inconsistently applied, sometimes omitted altogether.
- Currency formats, date encodings, and award breakdowns vary from country to country—and even from agency to agency.
Without enforced structural standards, data aggregators must build per-source parsers and reconciliation logic just to get to a usable baseline. This high-friction process emphasizes why many large organizations require specialized big data services company offerings to handle ingestion at scale.
Metadata Loss and Legal Gaps in Visibility
Key procurement metadata is frequently missing or malformed, creating risk exposure for downstream analysis and legal compliance.
- Timestamps are unreliable—some refer to publishing dates, others to deadlines or system log entries.
- Contract values are sometimes grouped or redacted, preventing proper cost comparison.
- Amendments are not always linked to the original tender, breaking auditability.
These metadata gaps turn legal risk into operational gaps in visibility, especially when trying to detect irregularities or supplier bias.
Threshold Aggregation Triggers Legal Constraints
Public procurement law distinguishes between below-threshold and above-threshold tenders. Mixing them during aggregation without care can break compliance.
- EU law sets strict publication and competition rules for tenders above certain financial limits.
- Below-threshold notices may follow simplified local rules or be exempt entirely.
- Aggregating both into one system without legal flags or filtering logic leads to misclassification risks.
A compliance-ready pipeline must segment tenders by jurisdiction and threshold logic before processing them as part of any data product.
Even the most advanced data pipelines break down if the source rules aren’t clear. Every step in the aggregation of tender data must map back to procurement law, not just format.
How to Aggregate Tender Data Effectively
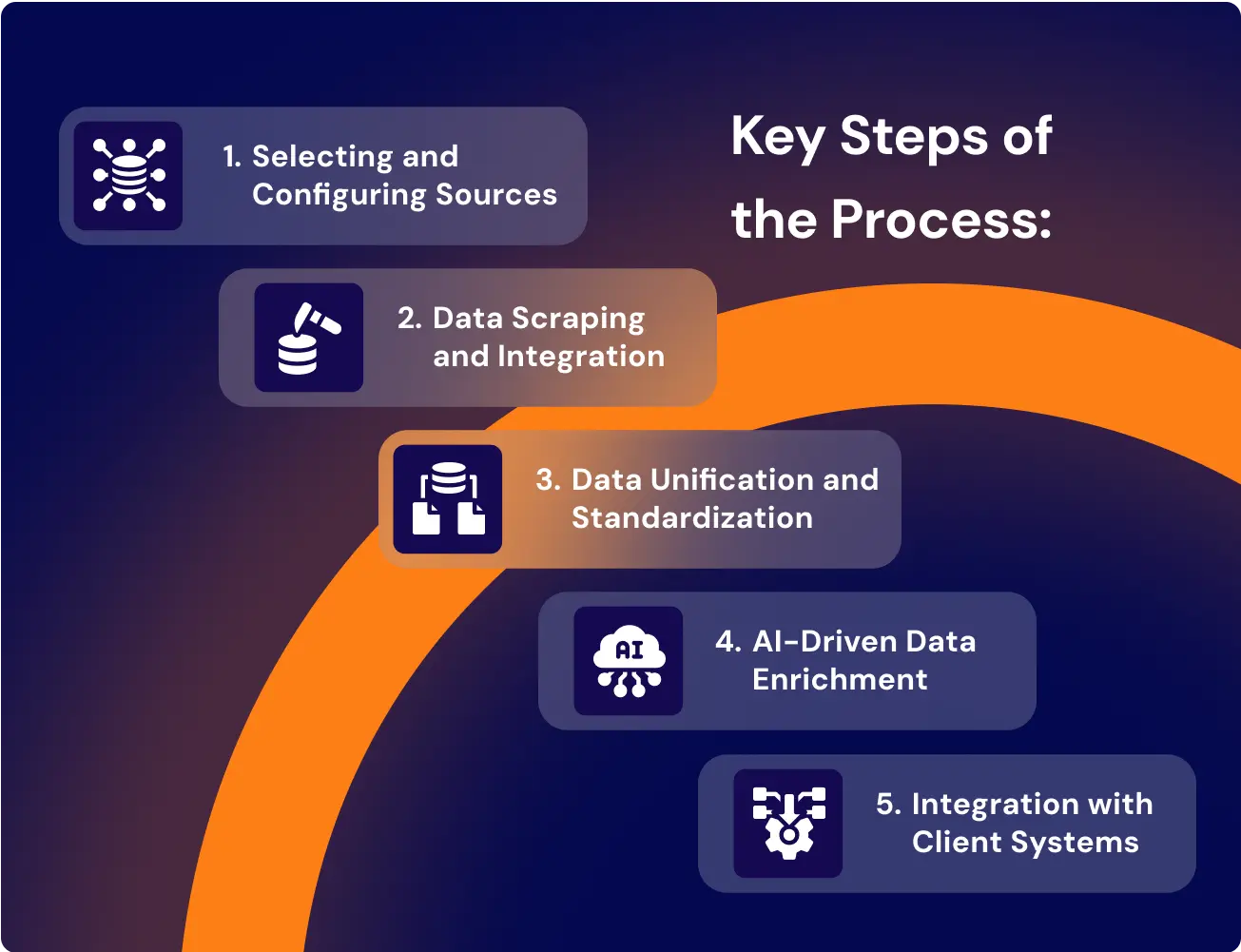
Building a robust aggregation workflow isn’t just about scraping or downloading tender notices. It’s about mapping source logic to procurement thresholds, standardizing metadata, and ensuring every step aligns with jurisdiction-specific compliance rules.
Aggregation only works if the system understands not just what it’s pulling, but why, from where, and under what rule.
Threshold Aggregation Triggers Legal Constraints
The first step in any aggregation workflow is identifying every source you need, across platforms, ministries, and languages.
- Build a source matrix by country, publication type (notice, award, amendment), and format (PDF, HTML, XML, API).
- Prioritize high-frequency and high-value sources—national portals, ministry registers, tenders electronic daily (TED) data aggregation for EU-level coverage.
- Track update frequency and archive retention to avoid loss of historical data.
Without a complete source map, downstream logic will be patchy, and thresholds or contract trails may be incomplete.
Normalize Data with Parsing Rules
Once raw data is collected, normalization turns it into usable infrastructure. This step removes format variability and aligns fields for processing.
- Convert local formats (dates, currencies, decimals) to unified standards.
- Use entity recognition for supplier names, departments, buyers, and contract types.
- Standardize fields like CPV codes, procedure types, and award amounts across all sources.
Parsed and normalized fields power comparison, deduplication, and analysis—turning raw entries into structured, auditable records. This structuring is implemented through a robust big data pipeline architecture designed for high-volume transformation.
Add Jurisdiction and Threshold Awareness
Each country or authority has its own procurement rules, especially around financial thresholds. Aggregation logic must respect this from the start.
- Flag each notice as above or below the threshold using country-specific rules.
- Tag procedures as open, negotiated, or direct award for legal classification.
- Create logic for alerts on non-compliant structures—e.g., negotiated procedures above the limit.
This legal tagging ensures your pipeline won’t just work—it’ll hold up under audit, investigation, or publication review. Ensuring correct and auditable data flow relies on effective data structures and transfer protocols, formalized in processes like ETL and data warehousing.
Automate Monitoring, Re-ingestion, and Error Handling
Even once built, no pipeline runs itself. Tender sites change frequently, breaking scrapers, formats, or field logic.
- Monitor DOM structure and format changes across each portal or API.
- Set re-ingestion rules to recover updated or corrected tenders.
- Log every failure, schema mismatch, or metadata gap for system-wide visibility.
Tender aggregation systems must include self-correction logic because portals update, thresholds change, and compliance rules evolve continuously. The foundational infrastructure for monitoring and scaling these processes is often provided through comprehensive data collection services partnerships.
When done right, the question of how to aggregate tender data becomes operational, not hypothetical. The right system builds in structure, legal segmentation, and update logic from the first step.
How to Aggregate Tender Data Effectively
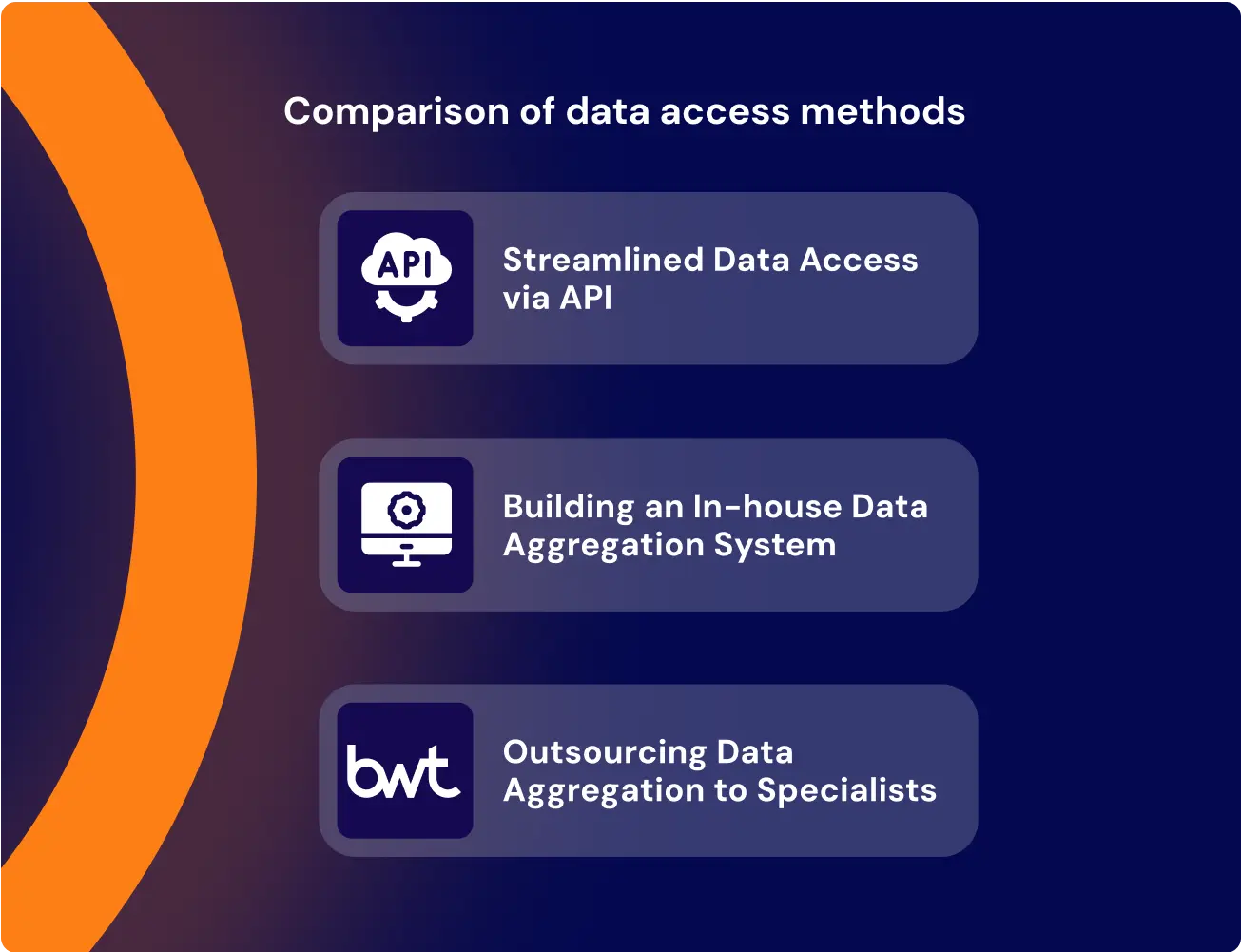
Aggregating tender data is only half the battle. Without a centralized data system, the output remains inaccessible to most teams, scattered across spreadsheets, folders, or disconnected tools.
Centralization isn’t about storing everything in one place. It’s about giving every role—from compliance to BI—a structured view of the same procurement logic. The core goal of centralization is to unify data across systems, which requires mature enterprise data integration capabilities.
A unified tender feed solution allows all departments—compliance, BI, legal—to access the same validated dataset without merging exports or syncing spreadsheets.
Design for Cross-Role Access and Searchability
Procurement, compliance, legal, and strategy teams each view tender data differently. A centralized system must meet all of them halfway.
- Build dashboards filtered by CPV, buyer, award value, and procedure type.
- Enable keyword search, legal flag filtering, and historical tender navigation.
- Add user-specific views: auditors see metadata history, analysts see supplier patterns.
When every team sees what they need—without spreadsheet exports or CSV merges—tender data becomes a shared asset, not a private dataset.
Centralize via API, Not Just UI
Many platforms stop at dashboards. But true centralization happens when systems talk to each other automatically.
- Set up API endpoints that expose normalized tender data by date, region, or tag.
- Allow internal systems (ERP, CRM, BI) to fetch and align with procurement data in real time.
- Include throttling, caching, and access control to protect stability and legal usage.
The centralized tender information system shouldn’t be another tool—it should feed existing workflows without creating bottlenecks or duplications.
Align Centralized Logic with Tender Data Aggregation
Centralization only works if the aggregation logic remains transparent and legally traceable.
- Display source alongside parsed and normalized data.
- Attach metadata lineage—what field came from where, when, and how it was transformed.
- Include threshold-based filters and country-specific rules inside the interface.
By aligning the centralized system with the underlying tender aggregation process, teams can trust that what they see reflects legal and operational truth.
Centralization is a logic layer, a source of truth, and a delivery mechanism. A well-built centralized data system turns procurement chaos into a search-ready infrastructure.
Automated Tender Insights Collection and Standardization
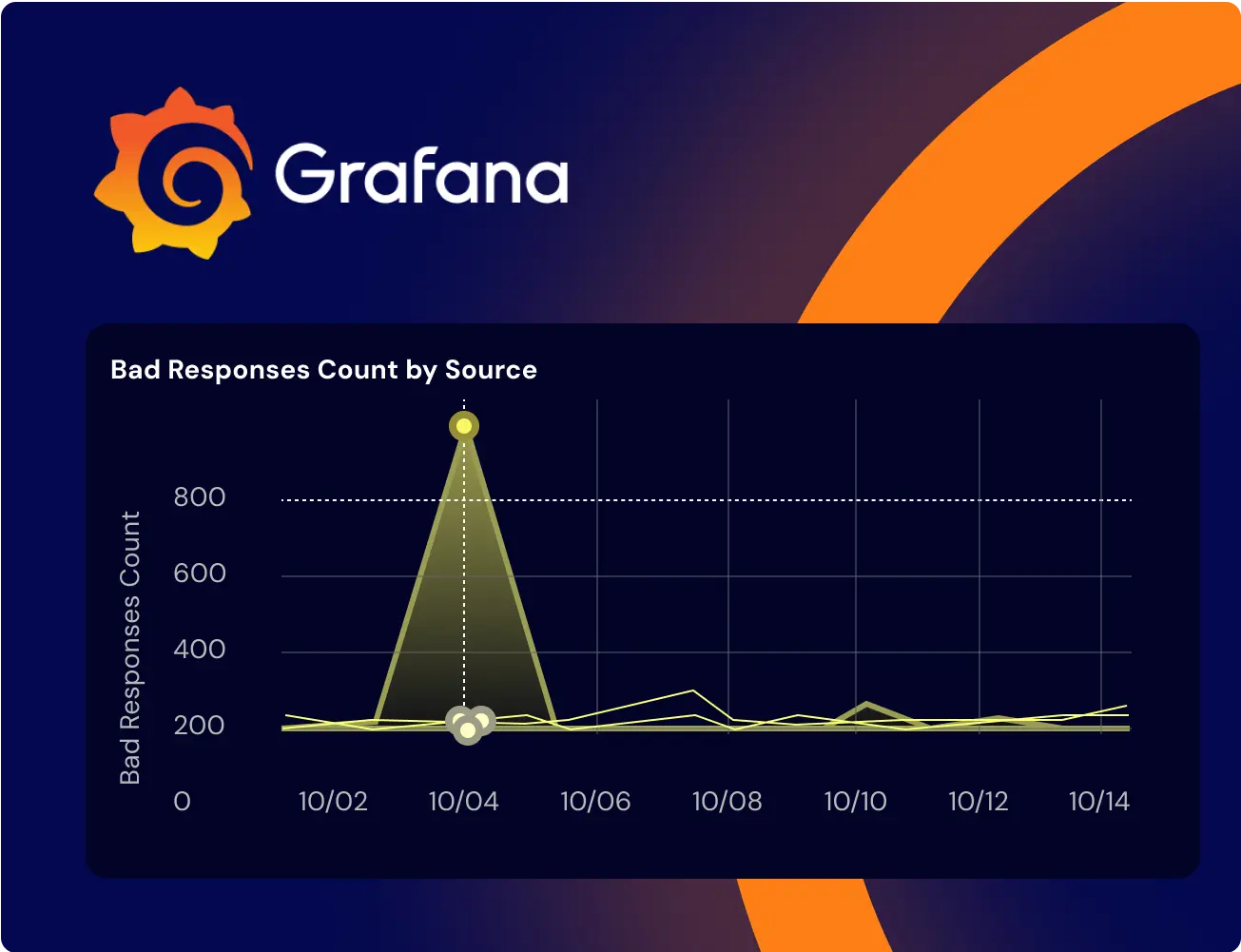
Manual collection of procurement data is no longer viable at scale. Authorities and vendors dealing with hundreds or thousands of notices per month need automated tender collection data pipelines. But automation alone isn’t enough. Without normalization and validation, automated data inflow can become a source of error rather than insight.
Grafana dashboards like the one shown above help monitor such data pipelines, revealing anomalies—such as sudden spikes in bad responses by source—that signal integration failures or upstream changes.
To handle the complexity of large external datasets, the principles used to build a custom data for a global analytics team are directly applicable to optimizing tender flows.
Automate Source Monitoring and Data Retrieval
Each portal or procurement registry comes with its quirks: rate limits, session logic, CAPTCHA layers, or export structures.
- Use scheduler-driven crawlers or API consumers to fetch new notices daily or hourly.
- Set smart retries, proxy logic, and failover mechanisms for unstable portals.
- Track document versioning to re-ingest updated tenders without duplicating records.
The collection engine should run without intervention, but log every attempt, update, and failure in audit-ready detail.
Standardize Structure at Ingestion
Once collected, each tender must be mapped to a structured schema. Without this, aggregated output is unusable downstream.
- Apply format recognition (PDF, HTML, DOCX, JSON, etc.) to route to the correct parser.
- Normalize date, currency, and value fields; assign CPV codes if missing or inconsistent.
- Extract and clean entity fields: buyer name, contractor ID, location, and contract status.
This parsing and structuring logic creates reliable, searchable fields—the foundation for all downstream analytics and validation.
Validate Data Against Compliance Rules
Standardization must respect procurement law. Automation without legal filtering can introduce high-stakes reporting errors.
- Detect missing fields or invalid logic (e.g., award before notice published).
- Check that values fall within expected thresholds for their jurisdiction.
- Flag high-risk entries: unusually low bids, short timelines, or repeat sole-source awards.
Compliance-first automation prevents legal exposure while ensuring your aggregation of tender data process remains transparent and trustworthy. The necessity for continuous validation is also demonstrated by the efforts to maintain accuracy for real-time telecom research address data feeds.
Automated collection means more than just speed. When paired with legal validation and structural standardization, it becomes the backbone of every serious tender analytics platform.
EU and International Context for Tender Aggregation
The European procurement ecosystem is undergoing rapid transformation, but remains structurally fragmented. Even with harmonization efforts like eForms and TED (Tenders Electronic Daily), the reality is that public buyers, vendors, and analysts still face technical and legal inconsistencies across borders. That’s why EU tender aggregation isn’t just an IT task—it’s a legal and strategic challenge.
Diverse Portals, Partial Compliance
Most EU countries maintain national procurement portals with their schemas, deadlines, and publication logic. While TED aggregates high-value cross-border tenders, it does not capture all below-threshold or regional-level data, leaving critical blind spots in market and compliance intelligence.
- TED often contains award notices but lacks amendments, making lifecycle reconstruction difficult.
- Local portals use non-standard XML, or publish notices as scanned PDFs that TED can’t parse.
- Language, currency, and CPV mismatches persist—even between neighboring states.
As a result, relying solely on TED means missing vast volumes of valuable procurement intelligence. When dealing with sensitive data across multiple jurisdictions, adherence to GDPR scraping principles is mandatory, especially for public procurement records.
The Role of TED and Its Aggregation Complexity
The tender electronic daily (TED) data aggregation pipeline isn’t plug-and-play. To extract full value, systems must:
- Parse multiple formats across TED XML, eForms, and legacy HTML archives.
- Normalize fields like procedure type, region, and buyer name into a multilingual schema.
- Track data lineage between TED data aggregation sources and local duplicates to avoid double-counting.
Even simple queries—like identifying recurrent sole bidders across France and Belgium—require deduplication, supplier mapping, and multilingual normalization across systems.
Legal and Operational Implications
Regulatory oversight demands traceability. Without tenders, electronic daily data aggregation that aligns with local context, it’s impossible to validate competition levels, trace procurement irregularities, or model fair access to public markets.
Moreover, public auditors and watchdogs increasingly rely on cross-jurisdictional insights. That’s where aggregating tender data becomes a legal infrastructure, not just a data product. Compliance segmentation is not only legal but operational, preventing the catastrophic mixing of sensitive and general information required for effective big data and data management.
To succeed across the EU, any tender aggregation system must go beyond TED. It must incorporate local nuances, handle multilingual normalization, and enforce eForms compliance, turning fragmented disclosures into cross-border procurement intelligence.
Conclusion: From Fragmentation to Strategic Control
Tender data aggregation it’s a foundational capability for any organization seeking visibility, fairness, and legal control across procurement landscapes. Whether you’re a national audit body, a regional buyer, or a pan-European compliance agency, your decisions are only as good as your data. And that data—today—is scattered, mismatched, and often legally risky without intervention.
We’ve shown that:
- Procurement still operates in silos, with fractured portals, formats, and inconsistent metadata.
- Aggregation of tender data enables actionable oversight—but only when done with legal and structural awareness.
- Fragmented notices can’t just be scraped—they must be normalized, parsed, and legally segmented to match jurisdiction-specific thresholds and procedures.
- EU tender data aggregation, especially across TED and local sources, brings international complexity—but also cross-border insight.
- A centralized tender data turns technical aggregation into strategic utility, making information usable by compliance teams, BI analysts, and legal auditors alike.
- Automated tender data collection with validation ensures your pipeline scales legally and operationally, without sacrificing trust.
The real challenge isn’t volume. It’s traceability. Aggregation must reflect legal thresholds, structural consistency, and audit-ready design. Anything less turns analytics into noise and risks into liabilities. To manage the entire data lifecycle from collection to deployment, executive teams rely on a partnership approach to data collection services that guarantees data flow and compliance.
At scale, the difference between a patchwork of scraped tenders and a unified, centralized, legally segmented data infrastructure is the difference between noise and insight—between reacting to procurement failures and proactively preventing them.
Whether your goal is compliance, transparency, or operational intelligence, tender data aggregation is where it starts.
Struggling with fragmented tenders?
We’ll help you build a scalable, audit-ready system aligned with procurement law.
Free consultation includes:
- Source audit & gap analysis
- Compliance & metadata mapping
- Architecture & automation plan
→ Book now to turn tender chaos into clarity.
FAQ
-
How to aggregate tender data?
To aggregate tender data, extract notices, awards, and amendments from multiple portals using scraping or APIs. Normalize fields (e.g., CPV codes, dates, supplier names) and link related records across sources. Store the cleaned data in a structured database with version control and legal tagging for compliance and analysis.
-
Why can’t I just use tenders electronic daily data aggregation or national portals directly?
Because even TED doesn’t cover the full tender lifecycle, especially for below-threshold contracts, amendments, or local procurements. National portals often publish in incompatible formats (PDF, non-standard XML), with missing or inconsistent metadata. Without aggregation, your view remains incomplete and legally risky.
-
What happens if I mix tenders below and above the threshold?
This creates legal misclassification. Above-threshold tenders are subject to strict EU-level rules; below-threshold ones may follow local exemptions. Aggregating them without segmentation leads to reporting errors, incorrect alerts, and failed audits. Every data point must be tagged by threshold logic.
-
Isn’t automation enough to solve this problem?
No. Automation without normalization and legal filtering creates more problems than it solves. Data inflows must be parsed, structured, and validated against jurisdiction-specific rules—otherwise, you’re scaling noise, not insight.
-
How do I ensure my aggregation pipeline stays compliant over time?
You need automated monitoring, schema change detection, re-ingestion logic, and audit logging. Procurement portals are constantly evolving, and your system must adapt accordingly. Without this, your pipeline breaks silently—and so does your compliance posture.






